|
Alcohol Health Effects –Impacting Nearly Every Organ Of The BodyAlcohol health effects occur for every organ system in the body. There are short term effects and long term effects. Short term effects involve small amounts of alcohol which change the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain reducing inhibitions and physical coordination. Long term effects of chronic alcohol intake involve much more serious changes in the body, such as damage to the heart, liver, gastrointestinal tract, and brain and for pregnant women fetal alcohol syndrome which has devastating consequences as part of alcohol health effects to the fetus.
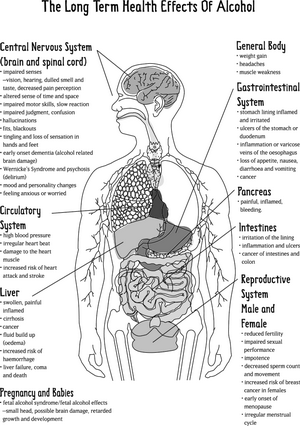
Alcohol Health Effects on the Brain and Nervous System Because small amount of alcohol is absorbed directly from the mouth into the blood stream, alcohol can diffuse easily into the brain, with almost immediate effects, reaching the brain about one minute after ingestion. Alcohol produces impairment in memory after just a few drinks, and the more an individual drinks the more the impairment increases. When large quantities of alcohol are consumed rapidly and on an empty stomach, a blackout can occur, leading to intervals where the intoxicated person can’t recall key details of events or entire events. Alcohol is soluble in fat, making it possible for it to cross the protective fatty membrane of nerve cells. Once the membrane is crossed alcohol can disrupt communications between nerve cells, throwing neurotransmitters out of balance by exciting and inhibiting nerve cells, causing sleepiness, loss of coordination, and impaired judgment and mental ability, and others tell the brain to keep drinking when it’s time to quit. These out of balance neurotransmitters probably in the short term contribute to a hangover and in the long term they probably contribute to addiction and withdrawal symptoms. Alcohol Health Effects on the Gastrointestinal System The chronic intake of alcohol and acetaldehyde leads to chronic irritation of protective mucosal linings of the gastrointestinal tract causing inflammation, release of free radicals, esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus) esophageal stricture or closure and difficulty swallowing that is common among alcoholics, gastritis also develops due to repeated exposure of the stomach to alcohol at high levels. There is also frequently diarrhea and malabsorption which is evidence of damage to the intestinal system. This leaves the mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines at a greater risk of cancer to these areas. Effect on the Liver The liver is almost entirely responsible for the metabolism and detoxification of alcohol, so it is not surprising that this organ suffers the most from chronic heavy drinking, resulting in chronic liver disease such as alcoholic fatty liver, acute alcoholic hepatitis, and alcoholic cirrhosis. Accumulation of fat in the liver is the early warning sign of liver damage.
Making dietary changes can help to treat fatty liver disease, and abstinence from alcohol is crucial. By reducing dietary fats there is some reduction of fat accumulation in the liver. By consuming adequate micronutrients and macronutrients this can help to speed the healing of the liver which is the body’s only organ that can regenerate itself when damaged if the damage is not too severe. When there is late stage liver disease then dietary restrictions of proteins may improve the symptoms of the disease or slow its progression. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Alcohol is particularly damaging in the early weeks of pregnancy and the consequences of the mother’s drinking are devastating to the fetus with resulting congenital birth defects, such as mental retardation, problems of coordination, heart, eye and genitourinary abnormalities, along with low birth weight, and a slowed growth rate. One obvious characteristic is facial abnormalities. Since a woman may not know that she is pregnant when drinking, health professional warn that women who are considering pregnancy or who are pregnant not drink alcohol during this time.
Next: For other information on nutrition some great references are: • Nutrition – Fourth Edition by Paul Insel, Don Ross, Kimberley McMahon, and Melissa Bernstein
Alcohol and Diet
|