|
Nutrients In Food – Vital For Life Vital For HealthWhat Are The Nutrients In Food? There are six classes of nutrients in food. The minimum diet must supply about 45 essential nutrients. These nutrient classes are carbohydrates, fats (lipids and oils), proteins, vitamins, minerals and water. The most important nutrient our body needs is water; we can’t survive long without it and will die without this essential nutrient.
The next most important category of nutrients that our body needs are carbohydrates, proteins and fats therefore these are called macronutrients. We need vitamins and minerals in less important quantities and these are referred to as micronutrients. Therefore, a more refined definition of nutrients is the essential chemicals in food that the body needs for the normal functioning of the body and good health and that must be obtained from food because they cannot be made by the body or cannot be made in sufficient quantities by the body. What Are The Characteristics Of The Macronutrients? Carbohydrates Chemical Formula of Carbohydrates
These macronutrients are a major fuel source for the body, made of the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Dietary sources of carbohydrates include the starches and sugars found in grains, vegetables, legumes (peas and dry beans), and fruits. Carbohydrates can be obtained from dairy products, but virtually none can be obtained from meats, they are a poor source of carbohydrates, but do provide other types of nutrients in food.
The body converts carbohydrates to a primary fuel, glucose, which is a simple sugar that provides energy to cells and tissues. Lipids Chemical Formula of Lipids
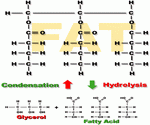
Lipids are also known as fats and oils and include substances in the form of nutrients in food such as cholesterol and phospholipids. These lipids are organic compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen like carbohydrates. These fats and oils known as triglycerides are another major fuel source for the body. Triglycerides, cholesterol, and phospholipids have important functions in the body such as to provide structure for the cells of the body and to carry fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E and K, In addition, cholesterol plays an important role in the making of hormones.
Dietary sources of lipids include the fats and oils that we use for cooking, the naturally occurring fats in meats and dairy products, and those from plant sources such as avocado, coconut and olives. Proteins Chemical Formula of Proteins
Proteins are organic compounds composed of smaller building blocks called amino acids. The structure of proteins contains nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. When we get amino acids from dietary proteins these combine with the amino acids that are made by the body to create hundreds of other different proteins in the body. These proteins then help to maintain the structures of the body, such as muscles and the heart, and to regulate body processes. A certain amount of protein can be used for energy, but protein is not a primary energy source. However, under conditions of starvation after other energy reserves have been used up, this is when the proteins in muscle begin to be consumed by the body for energy. Dietary sources of proteins as nutrients in food are found in the most concentrated sources in meats and dairy products. Other sources such as grains, vegetables, and legumes contribute proteins, and fruits contribute very negligible amounts, since these are high sources of natural carbohydrates. What Are The Characteristics Of The Micronutrients? Vitamins Vitamins are organic compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, and sometimes nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur and other elements. Vitamins regulate vital functions such as blood clotting, regulate calcium, energy production, and help to keep tissues and organs functioning and healthy. The role of vitamins is vital and the lack of a particular vitamin can have dire consequences for the body. Vitamins also help to extract energy from carbohydrate, fat, and protein.
There are two groups of vitamins, fat soluble vitamins A, D, E and K and water soluble vitamins C and the B vitamins. Vitamins can be found as a wide variety nutrients in foods such as fruits, vegetables, meats, grains, legumes, dairy products and fats. If a well balanced diet is eaten, then supplementing vitamins is unnecessary. The taking of some vitamins such as A, D, B6 or niacin can be harmful. Minerals There are at least 16 minerals that are essential to health, these substances are considered inorganic, and these minerals can be labeled as macrominerals those that are needed by the body in large quantities among them are sodium, chloride, potassium, calcium, phosphorus and magnesium, and microminerals, those that are needed by the body in trace amounts, among them are iron, zinc, copper, manganese, molybdenum, selenium, iodine, and fluoride. Minerals play vital roles in supporting the structure of bones and teeth and regulation of fluid balance and muscle contraction. Dietary sources of minerals as nutrients in food include animal foods such as meat and milk and also plant foods. Following a balanced diet is sufficient for most people to get all of the minerals needed. However, there are some cases where the diet may need to be supplemented for iron or calcium, but as with vitamins one should be careful since taking excessive amounts can be toxic to the body. Water Water is the simplest structure chemically; but water is the most important of all nutrients, without water there would be no life. The body can survive longer without food, but not very long at all without water. Water is essential to regulating temperature in the body, the lubrication of joints and the transportation of wastes and other nutrient. The body is nearly 60% water, thus regular water intake is needed to keep the body properly hydrated. Although water is found in beverages and other food products, the best source of water is water itself.
• Nutrition – Fourth Edition by Paul Insel, Don Ross, Kimberley McMahon, and Melissa Bernstein • Dictionary of Science by Hammond and Barnhart • Webster’s New World Encyclopedia – College Edition by Prentice Hall
Cooking Recipes
|
Nutrients
Most essential nutrient for life
Water

Macronutrients
Types of Carbohydrates
Grains

Vegetables

Legumes

Fruits

Types of Lipids
Dietary Fats in Oils/Meats

Dairy Products

Types of Proteins
Meats/Grains as A Protein Source

Micronutrients
Types of Vitamins
Naturally Occurring Vitamins

Types of Minerals
Meats contain minerals such as iron

Vegetables contain minerals such as phosphorus

Dairy products contain minerals such as calcium

Get great cooking tips and download your free ecookbook when you sign up for the Cooking Partner newsletter